In the world of software, licensing plays a crucial role in governing the distribution, use, and protection of software products. Software licensing defines the terms and conditions under which users can legally utilize software, ensuring compliance with intellectual property laws and safeguarding the rights of software developers and vendors. In this article, we will explore the different types of software licensing and delve into the legal considerations associated with them.
- Proprietary Software Licensing
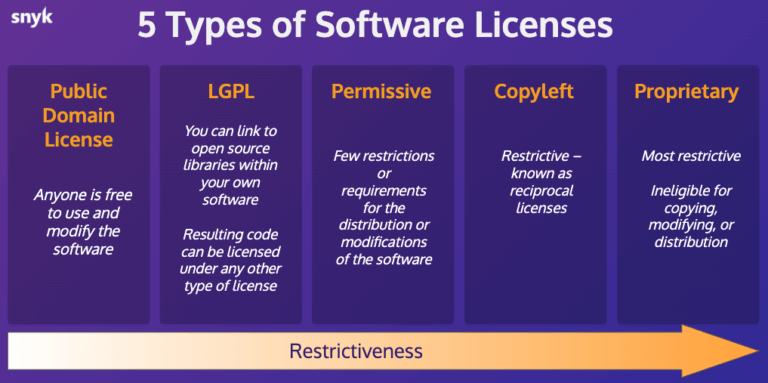
Proprietary software licenses are the most common type of software licensing. With proprietary licenses, the software is owned by the developer or vendor, and users are granted limited rights to use the software under specific conditions. These licenses often come with restrictions, such as limitations on copying, modifying, or redistributing the software. Examples of proprietary licenses include end-user license agreements (EULAs) and commercial software licenses.
Legal Considerations: When dealing with proprietary software licenses, it is crucial to carefully read and understand the terms and conditions outlined in the license agreement. Users must ensure compliance with usage restrictions, avoid unauthorized distribution or modification of the software, and respect any limitations imposed by the license.
- Open Source Software Licensing
Open source software licenses promote collaborative development and encourage the sharing of source code. Under open source licenses, users are granted the freedom to use, modify, and distribute the software freely. These licenses typically require that any modifications or derivative works also be released under an open source license, ensuring the continued availability of source code to the community. Popular open source licenses include the GNU General Public License (GPL), Apache License, and MIT License.
Legal Considerations: When using open source software, it is essential to comply with the specific requirements of the chosen open source license. Users should understand the obligations related to sharing modifications, providing attribution, and ensuring that any derivative works are also licensed under an open source license. Failure to comply with the terms of an open source license can result in legal consequences.
- Freeware and Shareware Licensing
Freeware refers to software that is available for use at no cost. Users are granted the right to use the software without payment, but the software remains the property of the developer or vendor. Shareware, on the other hand, allows users to try the software for a limited period before requiring payment for continued use. Both freeware and shareware licenses may come with certain restrictions and limitations specified by the developer.
Legal Considerations: While freeware and shareware may not require monetary payment, users still need to abide by the terms of the license agreement. It is important to understand any restrictions on the use, distribution, or modification of the software. Additionally, users should be cautious of potential malware or security risks associated with downloading and using freeware from untrusted sources.
- Subscription-based Licensing
Subscription-based licensing has gained popularity in recent years, particularly with cloud-based software and Software as a Service (SaaS) models. Under this licensing model, users pay a recurring fee to access and use the software for a specified period. The subscription typically includes updates, support, and maintenance during the subscription period. Once the subscription expires, users may no longer have access to the software.
Legal Considerations: Subscribers must understand the terms and conditions of the subscription agreement, including the duration, payment terms, and any limitations on usage. It is crucial to be aware of any automatic renewal clauses or cancellation policies outlined in the agreement.
- Enterprise Licensing
Enterprise licensing is tailored for organizations and businesses. Instead of licensing software on a per-user basis, enterprise licenses provide the organization with the right to use the software across multiple devices or for a specific number of users. Enterprise licenses often offer additional features, support, and customization options to meet the specific needs of the organization.