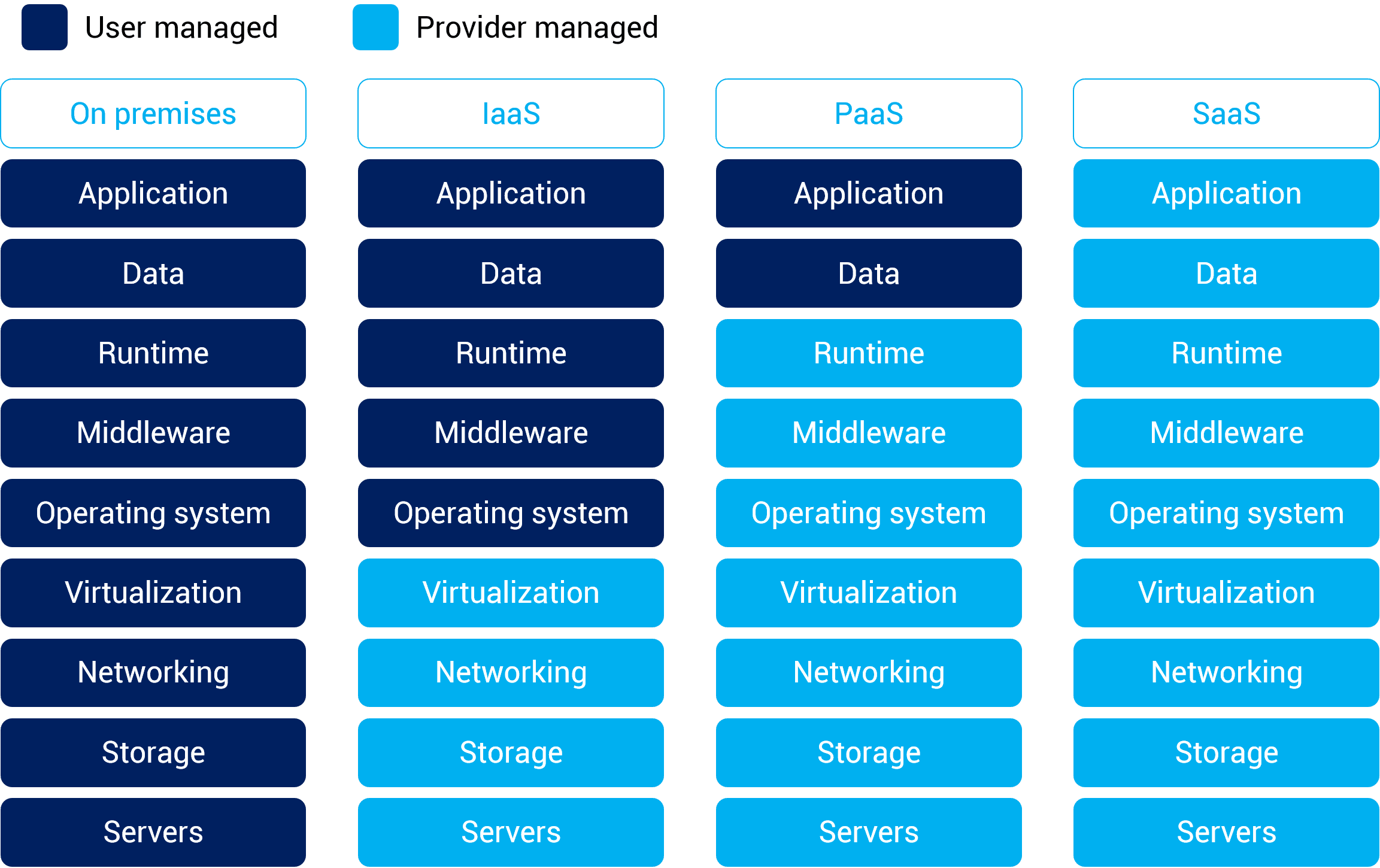
In recent years, the software industry has witnessed a significant shift towards cloud-based solutions. Software as a Service (SaaS) has emerged as a popular model that offers numerous advantages for businesses of all sizes. In this article, we will explore what SaaS is, its advantages over traditional software models, and important considerations for businesses when adopting SaaS.
- Understanding Software as a Service (SaaS):
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a software distribution model where applications are hosted and provided by a third-party vendor over the internet. Instead of purchasing and installing software on individual devices, users access the software through a web browser or a dedicated application. SaaS eliminates the need for upfront software licenses and hardware infrastructure, as everything is managed and maintained by the service provider.
- Advantages of SaaS for Businesses:
- Cost Savings: One of the primary advantages of SaaS is its cost-effectiveness. With SaaS, businesses can avoid substantial upfront costs associated with software licenses, hardware, and infrastructure setup. Instead, they pay a subscription fee based on usage or the number of users. This pay-as-you-go model allows businesses to scale their software usage and costs as their needs evolve.
- Scalability and Flexibility: SaaS offers businesses the flexibility to scale their software usage up or down based on their requirements. As businesses grow or expand, they can easily add more users or access additional features without the need for significant investments in infrastructure. SaaS providers handle the scalability and performance aspects, ensuring that businesses can focus on their core operations.
- Easy Deployment and Accessibility: With SaaS, software deployment becomes hassle-free. Businesses can access the software through a web browser or a dedicated application, eliminating the need for complex installations and compatibility issues. SaaS applications are typically platform-agnostic, making them accessible from various devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. This accessibility enables remote work and enhances collaboration among teams.
- Continuous Updates and Maintenance: SaaS providers take care of software updates, patches, and maintenance tasks, relieving businesses from these responsibilities. Updates and enhancements are deployed centrally, ensuring that all users have access to the latest features and security enhancements. This allows businesses to stay up-to-date with the latest technology advancements without the need for manual software updates.
- Improved Security and Data Protection: SaaS providers prioritize data security and invest in robust infrastructure and protocols to protect user data. They implement encryption, access controls, and backup mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information. Additionally, storing data in the cloud reduces the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or disasters. SaaS providers often have dedicated teams and resources to monitor and address security threats proactively.
- Considerations for Businesses:
While SaaS offers numerous advantages, businesses should consider the following factors before adopting SaaS:
- Integration Capabilities: Businesses should evaluate the integration capabilities of the SaaS solution with their existing systems and workflows. Seamless integration with other business applications, such as CRM or ERP systems, is crucial for data consistency and efficient operations.
- Customization and Extensibility: Some SaaS applications may have limitations in terms of customization and extensibility. Businesses should assess whether the SaaS solution can be tailored to their specific needs or if it provides APIs and integration options to extend its functionality.
- Data Ownership and Portability: Businesses should understand the terms and conditions related to data ownership and portability when using SaaS. It is essential to ensure that the business retains ownership of its data and can easily retrieve and migrate the data if they decide to switch to a different provider or deploy an on-premises solution.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): SLAs define the level of serviceavailability, performance, and support that the SaaS provider guarantees. Businesses should carefully review and negotiate SLAs to ensure they align with their requirements and expectations. SLAs should include provisions for uptime, response times, data backup, and customer support.
- Data Security and Compliance: Businesses must assess the security measures implemented by the SaaS provider to protect their data. This includes evaluating encryption protocols, access controls, data storage locations, and compliance with relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA. It is crucial to ensure that the SaaS provider meets the necessary security standards and follows industry best practices.
- Vendor Reputation and Reliability: Before selecting a SaaS provider, businesses should conduct thorough research on the vendor’s reputation, track record, and customer reviews. It is essential to choose a reputable and reliable vendor with a proven track record of delivering high-quality services and maintaining a stable and secure infrastructure.
- Data Backup and Recovery: While SaaS providers typically offer data backup and recovery services, it is crucial for businesses to understand the backup frequency, retention periods, and recovery procedures. Regular backups and robust disaster recovery mechanisms ensure that businesses can recover their data in case of accidental deletion, data corruption, or system failures.
- Exit Strategy: Businesses should have an exit strategy in place when adopting SaaS. This includes understanding the terms and conditions for terminating the contract, retrieving data, and ensuring a smooth transition to an alternative solution, if necessary.
- Best Practices for SaaS Adoption:
To maximize the benefits of SaaS adoption, businesses can follow these best practices:
- Thoroughly assess business needs and objectives before selecting a SaaS solution.
- Evaluate multiple SaaS providers and compare their offerings, pricing, and customer support.
- Involve key stakeholders, such as IT personnel, legal advisors, and end-users, in the decision-making process.
- Conduct a pilot or trial period to test the SaaS solution’s functionality, usability, and compatibility with existing systems.
- Ensure proper training and support for end-users to facilitate a smooth transition to the new software.
- Monitor the performance and usage of the SaaS solution regularly to identify any issues or opportunities for optimization.
- Stay updated with the latest developments and features offered by the SaaS provider to leverage new functionalities and improvements.
- Establish clear communication channels with the SaaS provider to address any concerns, report issues, and seek assistance when needed.
Conclusion:
Software as a Service (SaaS) offers businesses numerous advantages, including cost savings, scalability, easy deployment, continuous updates, and improved data security. However, businesses should carefully consider integration capabilities, customization options, data ownership, SLAs, security measures, and vendor reliability before adopting SaaS. By following best practices and considering these factors, businesses can successfully leverage SaaS to enhance their operations, productivity, and overall competitiveness in the digital landscape.